-
China’s robotics industry has fallen behind targets set out by Beijing in a plan to upgrade the industrial sector, despite production surging 19.1 per cent last year, research shows.
China buys and builds more industrial robots than any country, but its market is still dominated by Japanese companies, followed by manufacturers from Europe and South Korea, according to data from Shenzhen Gaogong Industry Research (GGII).
Robots produced by Chinese companies made up about 39 per cent of the domestic market last year, while Chinese computer chips were used in 45 per cent of locally-made machines, up from 12 per cent in 2016, according to the market research firm.
Beijing’s “Made in China 2025” plan, a strategy to upgrade the nation’s industrial sector and cut reliance on foreign technology, set a target for local robot manufacturers to supply half of the domestic market by 2020 and 70 per cent by 2025, by which time local robotics systems should be “perfected” to compete with global rivals.
-
Lynx & Co China-Swedish Robotic Assembly Line
-
What are Lighthouse factories?
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/09/manufacturing-lighthouse-factories-innovation-4ir/
-
Historic Building moved with robotic walking legs
CNN:
Workers had to first dig around the building to install the 198 mobile supports in the spaces underneath, Lan explained. After the pillars of the building were truncated, the robotic "legs" were then extended upward, lifting the building before moving forward. Over the course of 18 days, the building was rotated 21 degrees and moved 62 meters (203 feet) away to its new location. The relocation was completed on October 15, with the old school building set to become a center for heritage protection and cultural educationhttps://www.cnn.com/style/article/shanghai-relocate-building-preservation-intl-hnk-scli/index.html
-
Another look at the ChangAn Car factory
-
FULLY Automated Car FACTORY Tour in MEGACITY Chongqing
-
At a factory south of Japan’s Toyota City, robots have started sharing the work of quality-control inspectors, as the pandemic accelerates a shift from Toyota’s vaunted “go and see” system that helped revolutionise mass production in the 20th century.
Inside the auto-parts plant of Musashi Seimitsu Industry Co Ltd, a robotic arm picks up and spins a bevel gear, scanning its teeth against a light in search of surface flaws. The inspection takes about two seconds – similar to that of highly trained employees who check about 1,000 units per shift.
“Inspecting 1,000 of the exact same thing day-in day-out requires a lot of skill and expertise, but it’s not very creative,” the chief executive, Hiroshi Otsuka, told Reuters. “We’d like to release workers from those tasks.”
-
Worldwide industrial robots installation reached only 421,000 units in 2019, slightly lower than 2018's 422,000 units, marking the first on-year drop in seven years, according to figures from International Federation of Robotics (IFR).
Japan-based Fanuc, a top-4 robots brand worldwide, saw its six-month revenues ended September 30, 2019, slip 24.4% on year with net income also dropping 50.8% on year. Another top-4 robots brand Yaskawa also reported a 14.7% on-year decline for its six-month revenues ended on August 31, 2019 with its operating profits dipping 58.2% on year.
This is how capitalism work - until live ":robots" are available cheaper they'll stop any progressive movement.
-
The switch from Humans to Robots in China is on, robot sweatshop and Foxconn 8K panel factory being built
-
Customs thing is similar to patents in modern world. Mostly it feeds parasites.
-
Alibaba opens AI 'future hotel'
Chinese Internet giant Alibaba on Tuesday opened a hotel loaded with artificial intelligence (AI) and robots, automating a series of procedures like check-in, lights control and room service. FlyZoo Hotel, opened in Hangzhou, capital of east China's Zhejiang Province, where Alibaba is headquartered, is known as the company's first "future hotel".Customers can check into the hotel by simply scanning their faces. The facial recognition system installed in the hotel also enables customers to use their faces as key cards to open doors and access other hotel services. -
JD com progress
China-based online shopping operator JD.com began using over 20 smart self-driving robots to deliver merchandise items to purchasers in the Beijing area in late June 2018, according to China-based news reports.
Robots have pre-set route planning and will send messages to purchasers to pick up the items once they arrive at the destinations, the reports said, adding customer identity verification is done via facial recognition or keying in of codes.
JD.com has also employed heavy-duty drones to transport items to destinations around China in 24 hours, and such drones have payloads of 1-5 tons and flying endurance of over 1,000km.
-
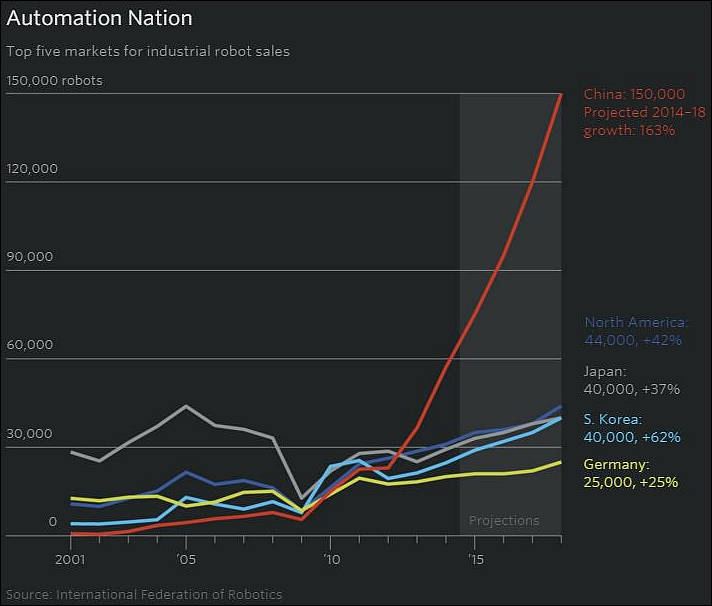
Global sales of industrial robots soared by 29% last year to hit a new record of 380,550, according to preliminary statistics released by the International Federation of Robotics (IFR). The 2017 sales were worth around $50bn.
The biggest driver of this increased demand has been China, where sales were 58% higher than in 2016, and 138,000 new industrial robots were installed during 2017. By comparison, sales in Germany were up 8% on 2016, with around 22,000 robots being sold. In the US, sales rose by 6% and 33,000 new robots were installed. During 2017, South Korea installed around 40,000 new industrial robots, while Japan added around 38,000.
Together, the five biggest markets – China, Korea, Japan, the US and Germany – accounted for 71% of all sales of industrial robots last year. The next five markets in order of size were Taiwan, Vietnam, Italy, Mexico and France.
-
Chine Post added 300 sorting robots this month


 sa558.jpg800 x 513 - 71K
sa558.jpg800 x 513 - 71K -
China produced 72,400 industrial robots in 2016 and 35,073 units in January-April 2017, increasing 34.3% and 51.7% on year respectively, Forward Business and Intelligence said, adding 34,000 locally produced industrial robots were sold in the China market in 2016 and the sales volume in 2017 is expected to increase to 43,000 units.
China was the world's largest industrial robot market from 2013 to 2016, with global market share rising from 20% in 2013 to 25% in 2014 and to 33.3% in 2016.
-
Results of 2016. Manufacturing robots production increase in 2016 was 34,3% in China. 2017 must be even better.
-
Automation is best solution to lower labor and land costs, says Kenmec chairman.
Hsieh pointed out that compared to those in the past, the automated production lines now have seen dramatic improvements. Robotic arms, instead of just making simple movements, now also feature visibility and computing capability.
Howdy, Stranger!
It looks like you're new here. If you want to get involved, click one of these buttons!
Categories
- Topics List23,964
- Blog5,723
- General and News1,342
- Hacks and Patches1,151
- ↳ Top Settings33
- ↳ Beginners254
- ↳ Archives402
- ↳ Hacks News and Development56
- Cameras2,361
- ↳ Panasonic990
- ↳ Canon118
- ↳ Sony154
- ↳ Nikon96
- ↳ Pentax and Samsung70
- ↳ Olympus and Fujifilm99
- ↳ Compacts and Camcorders299
- ↳ Smartphones for video97
- ↳ Pro Video Cameras191
- ↳ BlackMagic and other raw cameras121
- Skill1,961
- ↳ Business and distribution66
- ↳ Preparation, scripts and legal38
- ↳ Art149
- ↳ Import, Convert, Exporting291
- ↳ Editors191
- ↳ Effects and stunts115
- ↳ Color grading197
- ↳ Sound and Music280
- ↳ Lighting96
- ↳ Software and storage tips267
- Gear5,414
- ↳ Filters, Adapters, Matte boxes344
- ↳ Lenses1,579
- ↳ Follow focus and gears93
- ↳ Sound498
- ↳ Lighting gear314
- ↳ Camera movement230
- ↳ Gimbals and copters302
- ↳ Rigs and related stuff272
- ↳ Power solutions83
- ↳ Monitors and viewfinders339
- ↳ Tripods and fluid heads139
- ↳ Storage286
- ↳ Computers and studio gear560
- ↳ VR and 3D248
- Showcase1,859
- Marketplace2,834
- Offtopic1,319